-
E-mail:[email protected]
-

Telphone:+86-574-88073028
-

FAX:+86-574-88073029
QR code on
mobile phone
Welcome to Eastkey!
Welcome to Dongke!
LED mirror lights are commonly used in bathrooms, dressing rooms, hotels, and residential interiors where lighting is combined with reflective surfaces. Because these environments often involve moisture, frequent human contact, and long operating hours, safety becomes a primary concern. Two of the most discussed safety aspects are protection against electric shock and protection against overheating. Understanding how LED mirror lights address these risks helps users and installers make informed decisions and ensures safe long-term use.
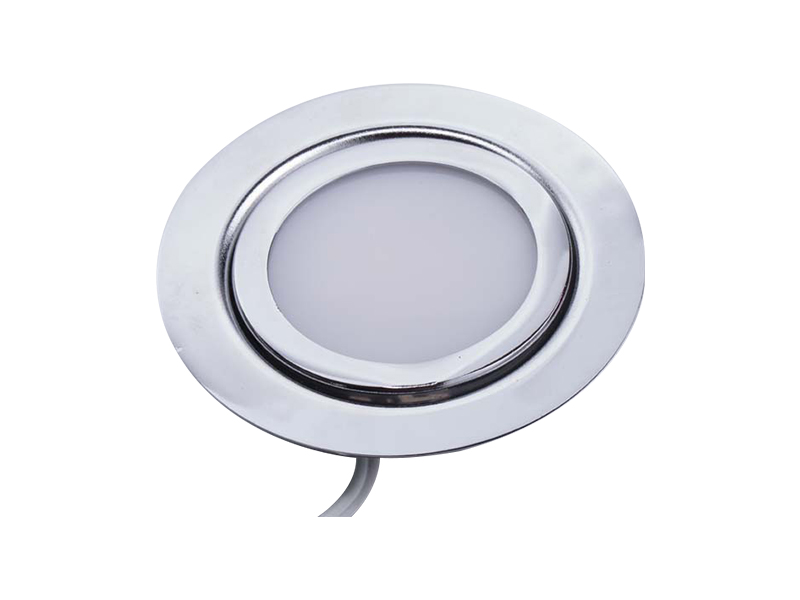
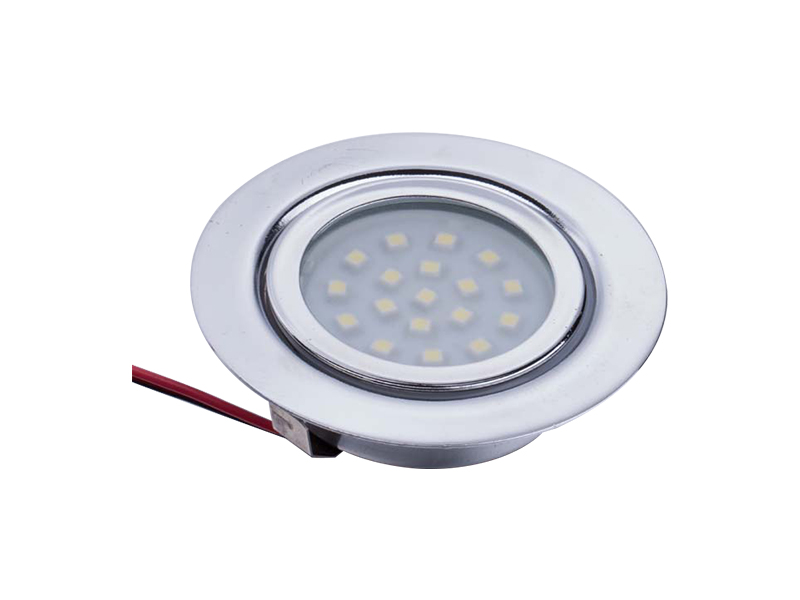
LED mirror lights typically consist of LED light sources, a power supply or driver, wiring, and a housing that integrates with or mounts near a mirror. The electrical design determines how current flows, how voltage is managed, and how heat is dissipated. Modern LED mirror lights are designed with low-voltage operation and controlled power conversion, which already reduces the inherent risk of electric shock compared to traditional high-voltage lighting solutions.
Bathrooms and similar spaces present higher electric shock risks due to water, humidity, and human proximity. Direct contact with live electrical parts or water ingress into the lighting system can increase the possibility of electrical hazards. LED mirror lights are therefore designed to minimize exposed conductive components and isolate electrical circuits from external contact. This design approach is essential for maintaining user safety in daily use.
Many LED mirror lights use insulation systems to reduce electric shock risk. Internal wiring is covered with insulating materials that resist heat and moisture. In some designs, double insulation is used, meaning two independent layers of insulation separate live components from the external surface. This structure reduces the likelihood that a fault inside the light will result in a live exterior surface, even if one layer of insulation becomes compromised.
A common safety feature in LED mirror lights is the use of low-voltage direct current supplied by an internal or external driver. The driver converts household alternating current into a lower voltage suitable for LED operation. Lower voltage levels significantly reduce the severity of electric shock if accidental contact occurs. The driver itself is usually enclosed and isolated, further limiting user exposure to electrical components.
Some LED mirror lights, especially those with metal housings, incorporate grounding or protective earthing. Grounding provides a controlled path for fault currents, reducing the risk of electric shock if insulation fails. In installations where grounding is required by local electrical standards, proper connection to the building’s earthing system plays a key role in overall safety. This measure works alongside insulation and enclosure design to enhance protection.
Protection against water and dust ingress is another important factor related to electric shock prevention. LED mirror lights often have ingress protection ratings that indicate their resistance to moisture. Sealed housings, gaskets, and protective covers prevent water vapor or splashes from reaching live electrical parts. This is particularly important in bathroom installations where condensation and splashing are common.
Although LEDs are more energy-efficient than traditional light sources, they still generate heat during operation. If heat is not properly managed, internal temperatures can rise, potentially affecting electronic components, shortening service life, or creating safety risks. Overheating protection focuses on managing thermal energy and preventing excessive temperature buildup inside the light.
LED mirror lights are designed with heat dissipation structures that transfer heat away from the LED chips and electronic components. Aluminum backplates, heat sinks, and thermally conductive materials are commonly used to spread and release heat into the surrounding air. Proper heat dissipation helps maintain stable operating temperatures and reduces the risk of localized overheating.
Many LED mirror lights include thermal protection elements within the driver or control circuit. These components monitor internal temperature and limit power output if temperatures rise beyond safe levels. In some designs, the light may automatically reduce brightness or temporarily shut down to prevent damage. This type of protection reduces fire risk and preserves component stability during prolonged use.
| Safety Aspect | Design Approach | Main Function | Risk Reduced |
| Electric Shock Protection | Insulation and low-voltage operation | Isolate live parts from users | Accidental electric contact |
| Moisture Resistance | Sealed housing and gaskets | Prevent water ingress | Short circuits and shocks |
| Overheating Protection | Heat sinks and thermal control | Manage internal temperature | Component damage and fire |
The materials used for the housing of LED mirror lights influence both electric shock and overheating protection. Non-conductive plastics reduce the possibility of electric contact, while metal housings are often combined with grounding and insulation. Housing materials also affect heat dissipation, as metals such as aluminum conduct heat more effectively than plastics, supporting thermal management strategies.
Even with built-in safety features, installation quality plays an important role in overall protection. Correct wiring, secure mounting, and proper sealing ensure that the designed safety measures function as intended. Poor installation may compromise insulation, create gaps for moisture entry, or restrict airflow needed for heat dissipation. Following manufacturer guidelines and local electrical standards is essential for maintaining safety.
The environment in which LED mirror lights are used affects both electric shock and overheating risks. High humidity, frequent temperature changes, and long daily operating hours place additional stress on electrical and thermal systems. Designs that account for these conditions through moisture resistance and thermal control perform more reliably in such environments. Users should also avoid covering or obstructing the light, as this may interfere with heat dissipation.
Over time, dust accumulation, aging seals, or degraded components can affect safety performance. Periodic inspection helps ensure that housings remain sealed and that there are no signs of overheating such as discoloration or unusual odors. Although LED mirror lights generally require minimal maintenance, basic checks support continued protection against electric shock and overheating.
Many LED mirror lights are designed to comply with electrical safety standards that address insulation, temperature limits, and moisture resistance. These standards guide manufacturers in implementing protective measures and provide users with confidence in product safety. Compliance does not eliminate all risks but indicates that the product has been designed with recognized safety requirements in mind.
User behavior also influences safety outcomes. Avoiding direct contact with electrical connections, not modifying the light or driver, and ensuring that damaged units are repaired or replaced all contribute to safer operation. Understanding the basic safety features of LED mirror lights allows users to recognize potential issues and respond appropriately.
LED mirror lights generally incorporate multiple layers of protection against electric shock and overheating through insulation, low-voltage operation, moisture resistance, and thermal management. These features work together to reduce risks associated with electrical use in sensitive environments. When properly designed, installed, and used, LED mirror lights provide functional illumination while maintaining a high level of operational safety.
top
E-mail:[email protected]
Telphone:+86-574-88073028
FAX:+86-574-88073029





